糖尿病合併症
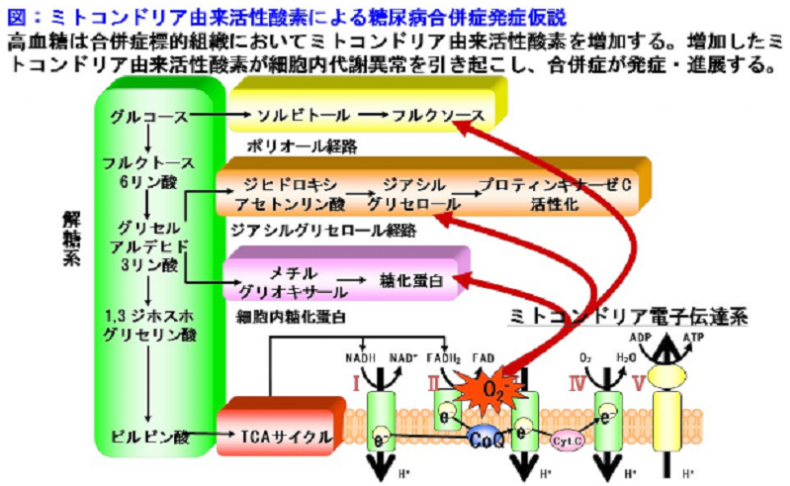
糖尿病合併症の発症を阻止するため、また合併症の新規治療法を開発するためには、糖尿病合併症の発症メカニズムを明らかにすることが重要です。現在まで、糖尿病合併症発症の主因が高血糖であることは明らかされています。ところが、高血糖がどのようなメカニズムで合併症を発症させるのかについては未だ一定の見解が得られていません。
これらの研究は私がニューヨークのアルバートアインシュタイン医科大学および熊本大学代謝内科に在籍中に主に行ってきたものです。現在は、当連携大学院において、この研究の続きである「高血糖とミトコンドリア電子伝達系からの活性酸素の関連を臨床的に証明する」ための新たな臨床研究の準備を進めています。
1.Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, Yamagishi S, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ, Hammes HP, Giardino I, Brownlee M. Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature. 2000;404(6779):787-90.
2.Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Brownlee M. The missing link: a single unifying mechanism for diabetic complications. Kidney international Supplement. 2000;77:S26-30.
3.Kiritoshi S, Nishikawa T, Sonoda K, Kukidome D, Senokuchi T, Matsuo T, Matsumura T, Tokunaga H, Brownlee M, Araki E. Reactive oxygen species from mitochondria induce cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human mesangial cells: potential role in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2003;52(10):2570-7.
4.Nishikawa T, Sasahara T, Kiritoshi S, Sonoda K, Senokuchi T, Matsuo T, Kukidome D, Wake N, Matsumura T, Miyamura N, Sakakida M, Kishikawa H, Araki E. Evaluation of urinary 8-hydroxydeoxy-guanosine as a novel biomarker of macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(5):1507-12.
5.Kukidome D, Nishikawa T, Sonoda K, Imoto K, Fujisawa K, Yano M, Motoshima H, Taguchi T, Matsumura T, Araki E. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase reduces hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2006;55(1):120-7.
6.Nishikawa T, Kukidome D, Sonoda K, Fujisawa K, Matsuhisa T, Motoshima H, Matsumura T, Araki E. Impact of mitochondrial ROS production on diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77 Suppl 1:S41-5.
7.Goto H, Nishikawa T, Sonoda K, Kondo T, Kukidome D, Fujisawa K, Yamashiro T, Motoshima H, Matsumura T, Tsuruzoe K, Araki E. Endothelial MnSOD overexpression prevents retinal VEGF expression in diabetic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;366(3):814-20.
8.Fujisawa K, Nishikawa T, Kukidome D, Imoto K, Yamashiro T, Motoshima H, Matsumura T, Araki E. TZDs reduce mitochondrial ROS production and enhance mitochondrial biogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;379(1):43-8.
9.Araki E, Nishikawa T. Oxidative stress: A cause and therapeutic target of diabetic complications. Journal of diabetes investigation. 2010;1(3):90-6.
10.Nishikawa T, Araki E. Mechanism-based antioxidant therapies promise to prevent diabetic complications? Journal of diabetes investigation. 2013;4(2):105-7.
11.Nishikawa T, Brownlee M, Araki E. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of early diabetic nephropathy. Journal of diabetes investigation. 2015;6(2):137-9.
12.Sada K, Nishikawa T, Kukidome D, Yoshinaga T, Kajihara N, Sonoda K, Senokuchi T, Motoshima H, Matsumura T, Araki E. Hyperglycemia Induces Cellular Hypoxia through Production of Mitochondrial ROS Followed by Suppression of Aquaporin-1. PloS one. 2016;11(7):e0158619.
13.Sakai K, Matsumoto K, Nishikawa T, Suefuji M, Nakamaru K, Hirashima Y, Kawashima J, Shirotani T, Ichinose K, Brownlee M, Araki E. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species reduce insulin secretion by pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;300(1):216-22.
14.Imoto K, Kukidome D, Nishikawa T, Matsuhisa T, Sonoda K, Fujisawa K, Yano M, Motoshima H, Taguchi T, Tsuruzoe K, Matsumura T, Ichijo H, Araki E. Impact of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 on insulin signaling. Diabetes. 2006;55(5):1197-204.
15.Nishikawa T, Kukidome D, Sonoda K, Fujisawa K, Matsuhisa T, Motoshima H, Matsumura T, Araki E. Impact of mitochondrial ROS production in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77 Suppl 1:S161-4.
16.Nishikawa T, Araki E. Impact of mitochondrial ROS production in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Antioxidants & redox signaling. 2007;9(3):343-53.